I'm here to talk about IpponGPT, what it is and how we built it. I can talk you about IpponGPT, a Bedrock + Langchain powered chatbot in our internal slack.
* Focused around providing a friendly experience
* Offers multiple pretrained LLMs for specific uses
Lets step back for a second to talk Finetunning VS Knowledge Base
https://www.emojisearch.app/ https://til.simonwillison.net/tils?
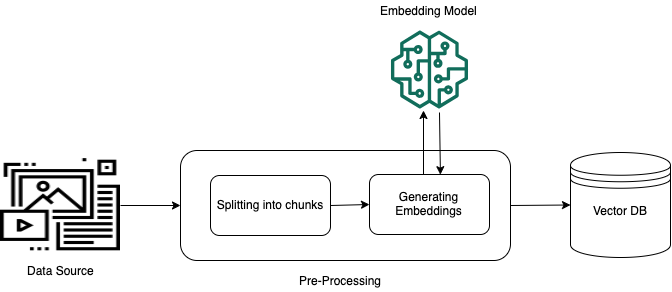
How do we go about: - Creating those embeds - Accessing them
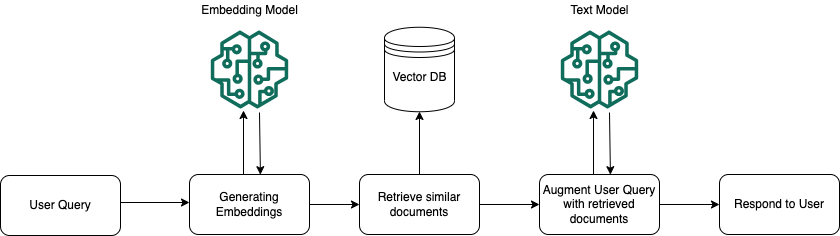
How do start putting these components together?